Problems in uncured concrete
Due to increase of temperature, thermal stresses will cause minor cracks in concrete
Loss of water due to evaporation in concrete will stop hydration of cement which decrease compressive strength.
Start of curing
Curing start after setting the concrete, three or four hours after placing the concrete is adequate.
Importance of curing:
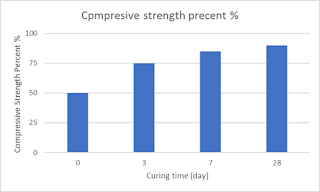
Experiments shows compressive strength of concrete structures increase with curing as shown in attached graph. Curing for 3 days reach 75% of cubic strength of concrete.
Factors affecting on curing
Evaporation in concrete is a main factor need to be controlled in curing, evaporation is affected by Temperature, wind and moisture, generally increasing evaporation above 0.5kg/m2 per hour will cause plastic cracks in fresh concrete.
Temperature also shall to be maintained above 5 Celsius degree to continue hydration reactions, otherwise increase temperature has a negative impact on cubic strength of concrete

Comments